Blog 8 - MEAN/MERN Stack
Intro
In last week’s blog post, I explained and walked through one of my past projects. We created a 2-tier LAMP stack using Docker/Docker-Compose. Today we’ll be discussing another type of full stack: MEAN/MERN.
What is MEAN/MERN?
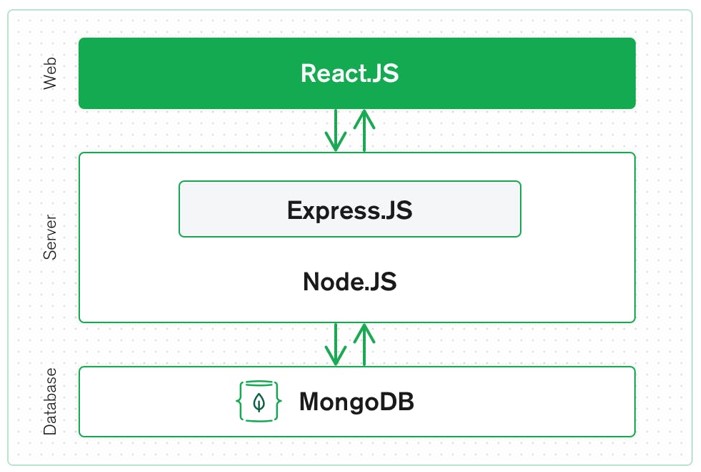
3-tier architecture of MERN stack
Just like how a LAMP stack is comprised of 4 software components, a MEAN/MERN stack is as well. However, a MEAN/MERN stack is a 3-tier architecture (front-end, application, and database) as opposed to LAMP’s 2-tier (application/web server and database). LAMP is a lower-level stack compared to MEAN/MERN because it defines the OS (Linux) and the web server (Apache). MEAN/MERN is a much higher level because it defines the front-end with Angular(JS) or React. Let’s take a look at each of the pieces:
- MongoDB
- This layer is the database; it’s at the bottom of all the other layers. It’s probably the biggest difference from a LAMP stack because it uses a NoSQL, document database instead of a SQL, relational database (like MySQL). MongoDB is designed to store JSON data natively.
- Express
- This layer is part of the server layer. Express is used to route HTTP requests to the appropriate handler. This means you can respond to HTTP requests to a URI endpoint by doing some pre-defined action. For example, let’s say we have a web app that stores user-inputted data on books. Thus, you might respond to a GET request to the
/bookendpoint by providing the list of all books in the database.
- This layer is part of the server layer. Express is used to route HTTP requests to the appropriate handler. This means you can respond to HTTP requests to a URI endpoint by doing some pre-defined action. For example, let’s say we have a web app that stores user-inputted data on books. Thus, you might respond to a GET request to the
- Angular(JS) / React
- This layer is the front-end which sits on top of the other layers. Both Angular(JS) and React handle connecting the UI with the program’s business logic. Using React means a simpler and advanced UI that handles data changes quickly. Using Angular(JS) means being able to handle a large, enterprise level app because of its use of MVC (Model View Controller) to create a complete architecture.
- Node
- This layer is another part of the server layer. It is situated below Express. Node is the web server framework that many JS frameworks are built on top of.
So why might you choose a MEAN/MERN stack over a LAMP stack? Well, you might choose a MEAN/MERN stack if:
- your data isn’t highly structured,
- MongoDB is a NoSQL database that stores it’s data in JSON format. It’s not meant for highly rigid data like what would be stored in a MySQL/MariaDB/etc database.
- you/your team is well-versed in JS (JavaScript),
- Express: JS, AngularJS: JS, React: JS, Node: JS. You get the point right? Each of the programming components all use JS. Even MongoDB is built for JavaScript Object Notation data. JS is the body and blood of this stack. This is great if you have a team of people who know JavaScript. It’s also great if you have full-stack developers because they won’t have to switch between HTML/CSS/JS then to Python/PHP when they go from front-end to back-end.
- you want to learn a modern stack.
- LAMP has been around for quite awhile. MEAN/MERN is becoming more and more popular as we seek web apps that are faster and more responsive.
Also, keep in mind that technology stacks aren’t exactly the most rigid outlines for web app development. You can pick and choose different components and create your own version of a stack. This is how MERN came to be; it’s just one of the many variations of the MEAN stack. Another is MEVN (V=Vue). Do the research and find out what works best for what you are trying to build.
Next Week
Again, I’m not sure what my next blog will be about, but stay tuned! I might talk more about JavaScript and my journey in learning it.