Blog 8: Studying for AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner pt.9

Intro and Recap
Hello again! This week we are continuing our discussion of the material that will most likely appear in the AWS Certified Cloud Pracitioner (CCP) Exam. Last time we went over a part of the eighth module, Databases, and briefly discussed the services of RDS, Aurora, Redshift, and DynamoDB. In this post, we’ll talk about Cloud Architecture. Let’s get started!
Cloud Architecture
In this module you go over some design principles and tools to help with building your architecture in the cloud. We’ll talk about the Well-Architected Framework, the concepts of reliability and high availability, and finally AWS Trusted Advisor.
Well-Architected Framework
The Well-Architected Framework is a guide for designing infrastructure that is secure, high performing, resilient, and efficient. It was created as a way to provide best practices after reviewing thousands of customers’ architectures. The framework is comprised of pillars, which each have a set of design principles and best practices. Currently, there are 6 pillars: Operational Excellence, Security, Reliability, Performance Efficiency, Cost Optimization, and Sustainability. The last pillar was just added as of December 2021. The mnemonic I came up with is: Only Striped Racers Perform Consistent Speed.
Let’s briefly go over the focus of each pillar. Operational Excellence is about running and monitoring systems to deliver business value. This means automating changes, responding to events, and defining standards to manage daily operations. Security is about protecting information, systems, and assets while delivering business value through risk assessments and mitigation strategies. This involves identifying and managing who can do what through privilege management, establishing controls to detect security events, and protecting confidentiality and integrity of data. Reliability means preventing and quickly recovering from failures and mitigating any disruptions that occur. Key topics include designing distributed systems, recovery planning, and handling changes. Performance Efficiency is about using resources sparingly while also meeting system requirements. This means selecting the right resources types and sizes, monitoring performance, and making informed decisions to maintain efficiency as business needs evolve. Cost Optimization’s focus is on eliminating unneeded expenses. You need to understand and control where money is spent, select the most appropriate and right number of resource types, analyze spending over time, and scale to meet business needs without overspending. Sustainability is about understanding the impact of the services used, quantifying the impact throughout the entire workload lifecycle, and working to reduce it. As you can see, there is some overlap between the focuses of each pillar. By upholding one pillar, you help to strengthen another. On the other hand, if you slack on one, you leave a greater burden on the others. You could compare the Well-Architected Framework to a house and its supporting pillars!
To dive deep into this topic check out the homepage. If you want a bit more info but not as much as the whitepapers, you can read this AWS blog post.
Reliability and High Availability
Let’s face it. No matter how well you plan out your system and workload, chances are it’s going to fail at some point and face downtime. The key is to plan for this ahead of time! But before we do that, we first have to understand some measurements to track how well our system is doing. Reliability is the measure of the system’s ability to provide functionality when desired by the user. In other words, it’s the probability that your entire system will function as intended for a specified period of time. We calculate this with Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). It’s the total time in service divided by the number of failures. Take a look at the graphic below for a visual.
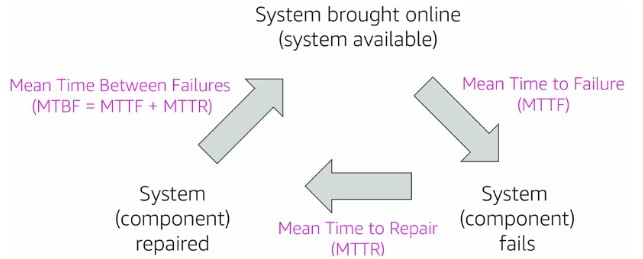
The cycle of failure and repair that systems go through
Availability is the uptime of a system over a set time period (usually 1 year). Being highly available means withstanding some degradation while still remaining available. Downtime should be minimzed and minimal human intervention is needed. Websites and applications usually have a status page where you can view their current and historical availability. Take for example, Github Status, PANW Cloud Services Status, and Discord Status. A common tool that’s used to do this is Statuspage from Atlassian.
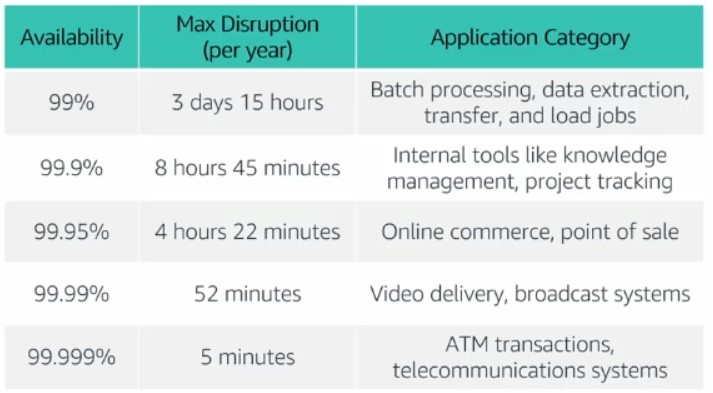
Chart for the recommended minimum availability each type of system should experience in a year
There are 3 factors that influence availability: fault tolerance, scalability, and recoverability. Fault tolerance is the ability for a system to remain operational even with some failures. This relies on built-in redundancy between system components. Scalability is the ability to accomadate growing capacity needs. Finally, recoverability is how the system restores service quickly and without losing any data.
Trusted Advisor
Now let’s talk about Trusted Advisor, a tool for providing real-time guidance on provisioning resources and following AWS best practices. Trusted Advisor looks at your account’s entire AWS environment and gives you recommendations in 5 categories: Cost Optimization, Performance, Security, Fault Tolerance, and Service Limits. With Cost Optimization it’ll do things like recommend reserving capacity and notifying you of any idle resources. With Performance it’ll look for any overutilized instances. In Security, it’ll examine your IAM permissions. Fault Tolerance will check for autoscaling, look at health checks, recommend multi-AZ deployments, and discuss backup capabilities. Service Limits will check for service usage that’s more than 80% the service limit. My mnemonic is Costly Performance Secures Faulty Service. It makes the most sense out of all the mnemonics I’ve created, I think. If you want a fun one there’s also Cyan Penguin Scares Five Seals.
The image below shows an example of the Trusted Advisor Dashboard.
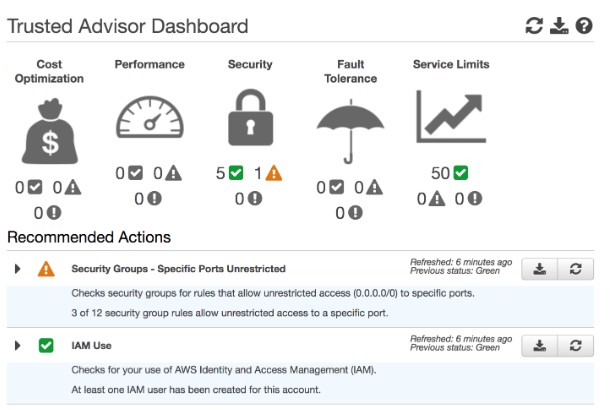
Trusted Advisor Dashboard shows recommended actions to take
Next Time
Hope you learned a lot today. Next module is the last! See you next week for the final AWS CCP discussion.
More Info
AWS Academy Cloud Foundations course
Note: Assets in this post are from AWS Academy’s Cloud Foundations course